In today’s fast-paced business landscape, integrating HR and payroll systems has become essential for organisations looking to boost efficiency and accuracy. Merging these two critical functions into a unified system not only streamlines administrative processes but also ensures that employee data transitions smoothly between HR and payroll functions.
This integration addresses common issues such as data discrepancies, compliance challenges, and manual errors, providing a comprehensive solution that simplifies management and enhances overall effectiveness.
In this article, we’ll delve into the advantages of integrating HR and payroll systems, the key considerations for successful implementation, and how this integration can contribute to organisational success by optimising workforce management and payroll accuracy.
What is HR?
Human Resources (HR) is a department within an organisation that plays a critical role in managing the various aspects of employee relations and development. One of its key functions is recruitment, where HR is responsible for finding and hiring the right talent to meet the company's needs. Once employees are hired, HR also manages onboarding, helping new employees integrate into the company and understand their roles.
In addition to recruitment, HR handles employee development by providing training and career growth opportunities. This helps employees improve their skills and advance in their careers, aligning their growth with the organisation’s goals. HR also takes care of compensation and benefits, which includes managing salaries, bonuses, health insurance, and retirement plans, ensuring that employees are fairly compensated and receive the perks that motivate them to stay with the company.
Another important function of HR is performance management. This involves evaluating employee performance, setting goals, and ensuring that employees are meeting the company’s expectations. Employee relations is another crucial area, as HR helps resolve disputes, address grievances, and maintain a positive work environment, which is essential for employee satisfaction and productivity.
What is payroll?
Payroll refers to the process by which a company calculates and distributes wages, salaries, and other financial compensation to its employees for their work during a specific period. It involves various tasks such as determining the amount of pay based on hours worked or salaries, withholding taxes and other deductions (like health insurance, retirement contributions, and social security), and ensuring employees are paid on time.
Beyond simply issuing paychecks or direct deposits, payroll also includes tracking and reporting on employee earnings, ensuring compliance with tax laws and regulations, and maintaining accurate records for auditing and legal purposes. Payroll is a critical function for maintaining employee satisfaction and ensuring a company’s financial and legal obligations are met properly.
In-house vs Outsourced Payroll
When deciding between **in-house payroll** and **outsourced payroll**, businesses must weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each option based on factors such as cost, control, and complexity.
In-house Payroll
In-house payroll refers to the process of managing all payroll activities internally within a company. This means that the company’s HR or finance team is responsible for calculating wages, withholding taxes, and ensuring employees are paid on time. In-house payroll often involves using dedicated payroll software and requires staff to be trained to handle the various complexities of payroll administration, compliance with tax laws, and reporting.
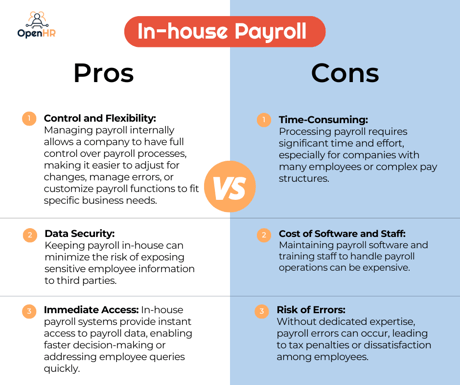
Pros:
1. Control and Flexibility: Managing payroll internally allows a company to have full control over payroll processes, making it easier to adjust for changes, manage errors, or customize payroll functions to fit specific business needs.
2. Data Security: Keeping payroll in-house can minimize the risk of exposing sensitive employee information to third parties.
3. Immediate Access: In-house payroll systems provide instant access to payroll data, enabling faster decision-making or addressing employee queries quickly.
Cons:
1. Time-Consuming: Processing payroll requires significant time and effort, especially for companies with many employees or complex pay structures.
2. Cost of Software and Staff: Maintaining payroll software and training staff to handle payroll operations can be expensive.
3. Risk of Errors: Without dedicated expertise, payroll errors can occur, leading to tax penalties or dissatisfaction among employees.
Outsourced Payroll
Outsourced payroll involves hiring a third-party provider to handle payroll tasks. This external company is responsible for calculating salaries, processing payments, managing tax filings, and ensuring compliance with labour regulations. By outsourcing payroll, companies can focus on core business activities while benefiting from the expertise and efficiency of specialized payroll providers.
Pros:
1. Time and Cost Efficiency: Outsourcing payroll allows businesses to save time and money, as external providers handle tax filings, compliance, and payroll processing efficiently.
2. Expertise and Compliance: Payroll providers specialize in handling the complexities of payroll regulations and tax laws, reducing the risk of mistakes or legal issues.
3. Scalability: Outsourced payroll can easily adapt to a growing business or handle payroll across multiple locations without additional internal resources.
Cons:
1. Less Control: Companies may lose some control over payroll processes, which can be a challenge when immediate changes or quick corrections are required.
2. Data Security Risks: Sharing sensitive employee data with third parties can increase the risk of data breaches or leaks, especially if the provider’s security measures are inadequate.
3. Cost of Outsourcing: For smaller businesses, outsourcing may seem more cost-effective, but fees can add up, especially for extra services or features not included in basic packages.
.png?width=477&height=400&name=pros%20and%20cons-%20%20(1).png)
Choosing between in-house and outsourced payroll depends on a company's specific needs, budget, and priorities regarding control, security, and efficiency.
How to integrate payroll software into your HR system
Integrating payroll software into your HR software can streamline operations, improve accuracy, and enhance efficiency in managing both payroll and HR tasks. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to do it:
1. Evaluate Compatibility
Before integration, ensure that both your HR software and payroll software are compatible. Some systems are built to easily integrate, but it’s essential to confirm whether they can exchange data seamlessly. Look for systems that support APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) for smooth integration.
2. Define Objectives
Clarify your goals for the integration. Whether you want to streamline payroll processing, automate tax compliance, or centralize employee data, understanding your objectives will help you choose the right integration tools and settings.
3. Map Data Fields
Identify which data needs to be shared between HR and payroll systems. Common fields include employee details (name, contact, bank info), salary data, tax information, attendance, and leave records. Ensure that both systems are aligned on the format and structure of the data fields.
4. Choose Integration Type
There are two main options you need to choose when you are looking to have an integrated HR and Payroll. Option 1 involves using a bundled HRIS and payroll solution, which streamlines implementation and reduces costs but may lack flexibility and scalability as a business grows. Option 2 recommends choosing systems with pre-built integrations, offering ease of use and scalability without requiring custom coding.
5. Choose Integration Method
There are a few different methods for integrating payroll with HR software:
- API Integration: This method connects both systems directly, allowing real-time data transfer and syncing between HR and payroll software. It’s the most flexible and efficient method.
- Third-Party Middleware: Some companies offer integration platforms that help connect two systems that might not be natively compatible.
- Manual Import/Export: If real-time syncing isn't necessary, some systems allow you to manually export data from HR software and import it into payroll software.
6. Test the Integration
Before fully rolling out the integration, run a pilot test. Check if the data flows correctly between the two systems, and ensure that any changes in employee information in the HR software automatically reflect in the payroll system.
7. Train HR and Payroll Staff
Once the integration is complete, provide training to HR and payroll staff on how to use the new system. Show them how data is shared between the two platforms, how to troubleshoot issues, and how to ensure the accuracy of data inputs.
8. Monitor and Optimise
After implementation, regularly monitor the integration to ensure it is working smoothly. Address any discrepancies or errors, and optimize settings as needed to keep data flowing correctly between the two systems.
By integrating payroll software with HR software, businesses can reduce manual entry errors, improve payroll accuracy, and gain real-time access to critical employee data.
OpenHR, your HR software that can integrate your payroll system
OpenHR, a leading provider of HR software, has partnered with IRIS, the UK's top payroll software provider, to offer a comprehensive HR and payroll management solution. This strategic collaboration combines the strengths of both platforms, providing businesses with a unified, efficient system that seamlessly integrates HR and payroll functions. By leveraging OpenHR's robust HR capabilities alongside IRIS's expertise in payroll, organizations can streamline operations and simplify administrative tasks.
With this integration, businesses will have access to a complete suite of tools designed to improve accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in both HR and payroll processes. Whether managing employee data, handling payroll calculations, or ensuring tax compliance, the combination of OpenHR and IRIS offers a seamless flow of information between systems, reducing manual work and minimising errors. This unified approach not only enhances productivity but also empowers HR teams to focus on strategic initiatives.

.jpg?width=1460&height=298&name=BANNERS%20DE%20CIERRE%20(6).jpg)